During the Mesozoic Era, the time of the dinosaurs, birds were indeed present on Earth, but their classification was quite different from what we know today. In fact, many scientists believed that birds were considered reptiles during the dinosaur days! This might seem strange to us now, but it’s a fascinating aspect of the history of life on Earth. Let’s explore this intriguing connection between birds and reptiles and uncover the secrets of their shared past.
The Origins of Birds
Birds are believed to have originated from a group of theropod dinosaurs during the Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. The earliest known bird is Archaeopteryx, discovered in Germany in 1861. It shared many characteristics with dinosaurs, such as teeth, a long bony tail, and claws on its wings. However, it also had feathers, wings, and a wishbone-shaped breastbone, which are distinctive features of modern birds.
The discovery of Archaeopteryx provided strong evidence for the theory of evolution and the link between birds and dinosaurs. Since then, many other early bird species have been discovered, including Confuciusornis and Microraptor. These finds have shed light on the gradual evolution of birds from their dinosaur ancestors, with changes in skeletal structure, feathers, and flight capabilities.
Birds and Dinosaurs: A Shared History

Birds and dinosaurs shared a common ancestor, and their evolutionary paths were intertwined for millions of years. During the Mesozoic era, which spanned from 252 million to 66 million years ago, dinosaurs dominated Earth’s landscapes, while birds evolved and diversified alongside them. Many dinosaurs, like Velociraptor and Oviraptor, had feathers, which were likely used for insulation and display purposes. Some scientists believe that birds may have evolved from a group of small, feathered theropod dinosaurs that lived during this time.
The shared history of birds and dinosaurs is evident in their skeletal structures, with many similarities in their hip bones, legs, and feet. Additionally, some dinosaurs, like Troodon and Dromaeosaurus, had bird-like characteristics, such as wishbone-shaped breastbones and three-toed limbs. The close relationship between birds and dinosaurs has led scientists to classify birds as a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs, highlighting their shared evolutionary heritage.
Characteristics of Early Birds

Early birds, like Archaeopteryx, shared many characteristics with their dinosaur ancestors. They had teeth, a long bony tail, and claws on their wings, which were likely used for grasping and perching. They also had feathers, wings, and a wishbone-shaped breastbone, which are distinctive features of modern birds. Early birds were likely omnivores, feeding on insects, seeds, and small animals.
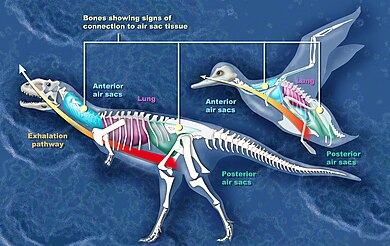
Despite their similarities with dinosaurs, early birds had some distinct characteristics. They had lighter skeletons, with hollow bones and air-filled cavities, which made flight more efficient. They also had more advanced respiratory systems, with lungs and air sacs that allowed for more efficient gas exchange. These adaptations enabled early birds to thrive in a variety of environments and paved the way for the diversification of modern bird species.
The Evolution of Feathers

Feathers are a distinctive feature of birds, providing insulation, support, and control during flight. They evolved from reptilian scales, with the first feathers likely appearing in small, feathered theropod dinosaurs during the Jurassic period. Early feathers were likely used for insulation and display purposes, with longer, more complex feathers developing later for flight.
The evolution of feathers was a gradual process, with many intermediate stages. Some dinosaurs, like Sinosauropteryx, had short, filamentous feathers, while others, like Microraptor, had longer, more complex feathers with quill knobs (where feathers attach to bone). The development of feathers was likely driven by selection pressures for insulation, display, and eventually, flight.
From Reptiles to Avians: The Transition

The transition from reptiles to birds was a gradual process that occurred over millions of years. It involved significant changes in skeletal structure, feathers, and flight capabilities. Early birds, like Archaeopteryx, shared many characteristics with their dinosaur ancestors, but also had distinct features like feathers and wings.
As birds evolved, they developed more advanced flight capabilities, with changes in wing shape, size, and musculature. They also developed more efficient respiratory systems, with lungs and air sacs that allowed for more efficient gas exchange. These adaptations enabled birds to thrive in a variety of environments and paved the way for the diversification of modern bird species.
Early Bird Species and Their Characteristics

Many early bird species have been discovered, each with unique characteristics and adaptations. Archaeopteryx, discovered in Germany in 1861, is considered one of the most important fossil discoveries. It had a combination of reptilian and avian characteristics, with teeth, a long bony tail, and claws on its wings.
Other early bird species include Confuciusornis, discovered in China in 1995, which had a distinctive beak shape and toothless jaws. Microraptor, discovered in China in 2000, had four wings, with feathers on its legs as well as its arms. These early bird species provide valuable insights into the evolution of birds and their diversification into modern species.
The Coexistence of Birds and Dinosaurs

Birds and dinosaurs coexisted for millions of years, with many species living alongside each other during the Mesozoic era. This coexistence was likely complex, with birds and dinosaurs interacting in various ways, such as competing for resources, predator-prey relationships, and possibly even symbiotic relationships.
Some scientists believe that birds may have evolved from a group of small, feathered theropod dinosaurs that lived during this time. This means that early birds would have lived among their dinosaur relatives, potentially competing with them for food and resources.
The Legacy of Dinosaur-Birds in Modern Times

The legacy of dinosaur-birds can be seen in modern bird species, which retain many characteristics of their ancient ancestors. Birds continue to evolve and adapt to their environments, with new species emerging and old ones becoming extinct.
The study of dinosaur-birds has also led to a greater understanding of evolution, adaptation, and the natural world. It has inspired new technologies, such as wing design and flight mechanics, and has captivated the imagination of people around the world.
The connection between birds and dinosaurs is a powerful reminder of the deep history of life on Earth and the incredible diversity of species that have evolved over millions of years. By studying the origins of birds and their relationship with dinosaurs, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and our place within it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the story of birds and dinosaurs is one of evolution, adaptation, and transformation. From their shared origins to their distinct characteristics, birds and dinosaurs have been intertwined for millions of years. The discovery of early bird species like Archaeopteryx and Microraptor has shed light on the gradual evolution of birds from their dinosaur ancestors, with changes in skeletal structure, feathers, and flight capabilities.
Today, birds are a diverse group of species, with over 10,000 different types found around the world. Despite their incredible diversity, they all share a common ancestor with the dinosaurs that roamed Earth during the Mesozoic era. The study of dinosaur-birds has not only deepened our understanding of evolution and adaptation but has also inspired new technologies and innovations.
As we gaze up at the birds flying overhead, we are reminded of the incredible history of life on Earth and the amazing transformations that have occurred over millions of years. The legacy of dinosaur-birds continues to inspire and captivate us, offering a glimpse into a fascinating world of ancient creatures and the incredible diversity of life on our planet.
FAQs
Q: What is the connection between birds and dinosaurs?
A: Birds evolved from a group of theropod dinosaurs during the Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. They share a common ancestor and have many similarities in their skeletal structure, feathers, and flight capabilities.
Q: What was the first bird species?
A: The first known bird species is Archaeopteryx, discovered in Germany in 1861. It had a combination of reptilian and avian characteristics, with teeth, a long bony tail, and claws on its wings.
Q: How did birds evolve from dinosaurs?
A: Birds evolved from small, feathered theropod dinosaurs through a gradual process of adaptation and transformation. They developed lighter skeletons, more advanced respiratory systems, and more complex feathers, which enabled them to fly.
Q: What is the significance of the discovery of Archaeopteryx?
A: The discovery of Archaeopteryx provided strong evidence for the theory of evolution and the link between birds and dinosaurs. It showed that birds did not appear suddenly, but evolved from a group of theropod dinosaurs over millions of years.
Q: How many species of birds exist today?
A: There are over 10,000 different species of birds found around the world, ranging in size, shape, color, and behavior.
Q: What is the legacy of dinosaur-birds in modern times?
A: The study of dinosaur-birds has led to a greater understanding of evolution, adaptation, and the natural world. It has inspired new technologies, such as wing design and flight mechanics, and continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world.
Q: Can birds still be considered dinosaurs?
A: Yes, birds are a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs and can still be considered dinosaurs. They have retained many characteristics of their ancient ancestors and are a living example of the incredible diversity of life on Earth.



